<<back
Chapter 4
User Guide
A. Arrangement of the Lesson Plans
The lesson exemplars contains 36 samples of Lesson Plans, which are written by Southeast Asian experts with different educational systems, cultures, ethics, and religious traditions. Such a rich environment is depicted in the development of HVWSHE lesson plans and materials which are mainly based on good practices in the SEAMEO countries with diverse socio-cultural background and learning contexts (Table 1).
The variety of the Lesson Plans are organized by country and thematic strands of HVWSHE, i.e., the eleven Southeast Asian countries are arranged in alphabetical order, and the then followed by the four thematic strands within each country.
The following four thematic strands were addressed in the lesson plans:
- Water, environmentally-sustainable development,
- Water, social equity and human dignity,
- Water for health, sanitation and recreation, and
- Water in culture, traditions and religious practices.
The Lesson Plans are intended for primary and secondary school teachers to implement the integration of HVWSHE into their teaching and learning process. The plans do not come with textbooks, and so they are self sufficientin the lesson materials to meet learning objectives. It can be expected that there will be differences of subjects, topics and levels of students in the point of view of each SEAMEO country, thus modification maybe necessary. In its implementation, the plan may need to be supported by use of relevant contextual references to enrich students’ knowledge and skills.
Table 4.1. List of Lesson Plans of HVWSHE
No |
Country |
Strands |
Water, environmentally-sustainable development |
Water, social equity and human dignity |
Water for health, sanitation and recreation |
Water in culture, traditions and religious practices |
1. |
Brunei |
Topic: Earth Resources
Subject: Science
Grade: 6 |
Topic: Water Purification
Subject: Science
Grade: 7 |
Topic: Water in Nature, the Three of Water and Water Cycle
Subject: Science
Grade: 7 |
Topic: Effects of Human on the Ecosystem, Pollution, and Conservation
Subject: Biology
Grade: 10 |
2. |
Cambodia |
Topic: The Poor Farmer
Subject: Khmer Language
Grade: 4 |
Topic: Food, Nutrition, and Clean Water
Subject: Home economic
Grade: 7 |
Topic: Importance of Using Clean Water and Preventing Pollution
Subject: Moral Civics
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Benefits of Water
Subject: Multi-subject (application of science and social study).
Grade: 6 |
3. |
Indonesia |
Topic: Water Pollution
Subject: Biology
Grade 7 |
Topic: Hand Cleanliness
Subject: Sanitation and Physical Education
Grade: 2 |
Topic: Water Conservation
Subject: Civics Education
Grade: 7 |
Topic: The Use of Water in Religious Practices (Ablution)
Subject: Islam Religion
Grade: 2 |
4. |
Lao PDR |
Topic: The importance Source of Water in Lao PDR
Subject: Science, Lao Language, and Art
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Food and Water
Subject: World Around Us
Grade: 1 |
Topic: Excretion
Subject: World Around Us
Grade: 1 |
Topic: Water in Culture, Tradition, Religious Practice, on Saving and Conserving water
Subject: Art, Science, Moral Education, Lao Language, Mathematics, and Geography
Grade: 3 |
5. |
Malaysia |
Topic: The Effects of Water Cycle on Man and Marine Life
Subject: English Language
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Water Pollution: Causes and Effects
Subject: English Language
Grade: 9 |
Topic: Healthy Body, Healthy Mind
Subject: Health Education
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Graphic design: poster
Subject: Visual Arts
Grade: 9 |
6. |
Philippines |
Topic: Ways of Cleaning Oil Spills
Subject: Chemistry
Grade: 3 |
Topic: How Pollutants Alter the Properties of Water
Subject: Science
Grade: 3 |
Topic: Water as a Basic Need of Man
Subject: Makabayan
Grade: 5 |
Topic: Using Physical Change (Distillation)
Subject: Science and Health
Grade: 3 |
7. |
Singapore |
Topic: Evaporation, Transpiration, Condensation, Precipitation, Runoff, Hydrological Cycle
Subject: Geography
Grade: 7 |
Topic: Scarce Resource, Domestic and Non-Domestic Usage, Conservation
Subject: Geography
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Scarce Resource, Water Constraint, Technology
Subject: Geography
Grade: 8 |
Topic: Catchments Areas, Vulnerability, International Agreement, Technology, Recycling, Desalination
Subject: Geography
Grade: 8 |
8. |
Thailand |
Topic: Mapping Water Resource In School
Subject: Social Studies, Language And Arts
Grade: 4 |
Topic: Explore About The Water Consumption
Subject: Social Studies, Language And Arts
Grade: 4 |
Topic: Water Issues In School
Subject: Social Studies, Science, Language And Arts
Grade: 4 |
Topic: Culture, Beliefs, and Tradition Of Water Conservation
Subject: Social Studies, Mathematics, Thai Language And Arts
Grade: 4 |
9. |
Vietnam |
Topic: Saving and Protecting Water Resources
Subject: Moral Education
Grade: 3 - 5 |
Topic: The Causes of River Water Pollution
Subject: Geography
Grade: 7 - 9 |
Topic: Polluted Water
Subject: Material And Energy
Grade: 1 |
Topic: Protect Water Resources
Subject: Environment And Natural Resources
Grade: 1 |
The Lesson Plans consist of three main steps of learning activities, i.e., introduction, main activities (lesson proper), and closure with the given time duration for each step to be well managed for students to get best achievement as required by learning objectives of HVWSHE. Assessment/evaluation methods are provided at the end of the Lesson Plans to gain information about achievement of students in both subjects and HVWSH.
A.1 Introduction
The purpose of this session is for the teacher to prepare students to be ready or to get engaged for the class. It can be conducted by checking the presence of students, showing the importance of the topics, motivating students to master the topics, or asking questions related to the topics for drawing students’ attention or warming them.
A.2. Lesson Proper
Lesson proper contains teaching materials and strategies which could include learning materials and media as well as teaching - learning methods and approaches. The materials and approaches may need modification for students from other countries. In these cases teachers should be flexible to adapt learning materials, media, and strategies.
Teaching and learning will be effective when students have their own experiences on concepts, principles or theories about the topics. Students should not passively get the concepts or listen to teachers telling them the concepts. They should dominantly take part in the building of concepts by themselves. Two ways interaction between teachers and students must occur where students should even dominate, but should not in another way around. Therefore, teachers are required to provide or create natural resources for students to observe. These approaches are usually called contextual teaching and learning, which have been widely used as effective approaches in Science teaching. Beside that, constructivism contextual teaching and learning has also been proven as successful approaches applied in primary and secondary schools in the Philippines (Pannen 2002). Thus, the enclosed Lesson Plans are predominantly based on contextual and constructivism approaches.
Contextual and constructivism approaches require students to get best achievement in all three important domains of learning; cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. With this approach, students should be able to organize, manage, proceed, and communicate their learning achievement, and be able to implement it into real life.
A.3. Closure
This session is made to finalize learning process and as a transition to the next learning experience. Teacher is expected not to dominate the process of summarizing learning when students had their own observation about the topics. Teacher is encouraged to motivate and facilitate students to create their own conclusion, since constructivism teaching and learning requires students to build concepts from their own experiences. In this case, the responsibility of teacher is to make comment and eto put emphasis on the students summary.
A.4. Time Duration
Time duration written in Lesson Plans is not an absolute measure since some factors such as class situation, learning materials, availability of facilities, and students’ condition must also be considered. Therefore, the time duration can be modified to the need of teaching and learning process to produce best results in cognitive, affective, and psychomotor in HVWSH as well as the topic itself.
A.5. Assessment / Evaluation
Assessment provided in Lesson Plans are intended as an alternative measure of learning outcomes, to measure whether or not students learning outcomes meet learning objectives. In case the assessment methods are not suitable for the given students, teachers are welcome to develop their own assessments.
B. Exemplars of HVWSHE Lesson Plans and the Process of Development
Thirty six lesson plans have been prepared by teachers and education experts from SEAMEO countries based on problems of human values in water, sanitation, and hygiene education in Southeast Asian schools. The preparation was facilitated by United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT) and Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization (SEAMEO) in cooperation with Asian Development Bank (ADB).
Development of teaching and learning materials in HVWSHE was firstly conducted in the Workshop on Teaching and Learning Materials Development which was organized by SEAMEO INNOTECH, Philippines. The materials produced were then reviewed in the Review Meeting hosted by SEAMOLEC in Jakarta. Detail of steps of the development is given in Figure 4.1.
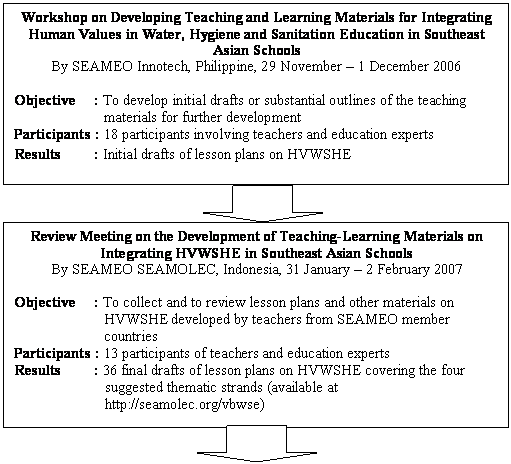
Figure 4.1. Process of the Development of Teaching and Materials in HVWSHE
C. Integrating Human Values and Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Education in Southeast Asian Schools
Evangelista (2006) emphasized that the values integration serves as a a channel of values development through the teaching-learning activities in the different subject areas. This line of thought has been in line to Parahakaran (2006) and Herbard (in Sadker and Sadker, 1991) who state that values education will be effective when they are taught inherently in instruction for the development of good people. Evangelista further shows examples of effective HVWSE in the lessons of Mathematics, Science, English, Social Studies, and Home Economics.
Integration of human values and water, sanitation, and hygiene education aims to help students to:
- Understand the concept of human values in water education and the ways to make the concept operational in various education streams, levels and delivery modes.
- Gain insights on the current global and regional initiatives relating to sustainable use of water and maintaining water resources.
- Have a working knowledge of integration and contemporary approaches to enhance learning effectiveness
- Try-out, apply or modify the examples given in the resource pack and document the results.
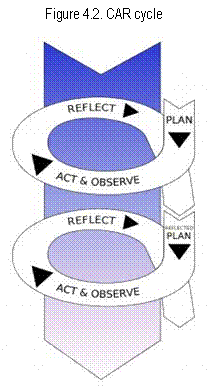
The process of integration of Human Values and Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Education into the school subjects under four thematic strands can be best described as a classroom action research (CAR) activities by the teacher (Kemmis and McTaggart, 1988). The first step in CAR is the planning step. It requires teachers to design and preparer all steps of teaching and learning process from planning to assessment, and other supporting components of instructional system to guarantee that teaching and learning process will take place.
In the planning step, teachers may use variety of available learning resources to support their teaching and learning. In this case, the exemplary lesson plans serve as one of the learning resources for teachers in the planning step. Lesson plan is to help students to reach their best achievements, which include all learning experiences provided for students, i.e. teaching-learning strategies, learning resources and environment, assessments / evaluation techniques, and various supporting systems. Lesson plan will help teachers to structure the learning for themselves and for students, and to help with the flow of the class, especially when something has occurred to distract everyone, including the teacher. It has been reported that students get benefit from and appreciate well structured lesson. Teachers may take a look at the existing lesson plans in this book, review the plans, and model their plan after the existing lesson plans. They may want to make modification as much as possible to relate to the local needs. They may also write their own plan creatively which is totally different from the existing lesson plans.
Before they go to the classroom for their teaching and learning process, they may want to act and observe on examples of implementation of integration of HVWSHE in the teaching and learning process. Part of the action and observation is conducted via the Training of Trainers conducted by SEAMEO RECSAM. The other part will be when they are training other teachers, and they are also carrying out the implementation by themselves.
Afterwards, teachers are expected to do a reflection on overhauling their teaching and learning process, their integration strategies, and the overall results of their teaching and learning process. The insights gain through this process can be useful and of highly important to the improvement of the lesson plan for the subsequent teaching and learning process. The cycle can be repeated as many times as necessary.
The CAR cycle is expected to be not only implemented in this context of integration of HVWSHE into the teaching and learning process, but also to be implemented regularly by teachers in every teaching and learning process. It hopefully can assist improvement of the quality of students learning as well as the teachers’s teaching and learning process.
Each SEAMEO country can implement the lesson plans provided in this book. Since human values can be taught inherently in instructional model (Parahakaran 2006) and in various subject areas (Evangelista 2006), teachers are expected to be prepared and able to create their own plans for any subject or topic which are not provided in this book.
D. Structure of the Lesson Plans
A summary of the content of the lesson plans analyzed by thematic strands is provided in the next chapter of this book. However, in general, the structure of the lesson plans in this book are as follows:
1. Overview and Background Information
- The section give the background/context for the particular lesson, how it relates to the other components/units in the curriculum, and the baseline knowledge/skills that the students would need in order to optimally learn and actively participate in the lesson.
- Some explanatory notes to show how the lesson relates to the learning goals in the core learning area (science, mathematics or social studies) as well as the human values that are built into the lesson.
- Some suggestions on variations of the lessons and the insights gained by a teacher in applying the lesson.
- In outline form, the following background information is provided:
- Specific component(s) in the curriculum/syllabus (some countries have specific section/paragraph references)
- Subject (Learning Area)
- Grade/Year Level
- Teachers Notes: additional information on how the lesson is linked with some country- or culture-specific event (e.g. national holiday, school-wide activity) and related lessons in other subject areas.
2. Formatof Lesson Plan
Examples: the water cycle
converting English to metric scale
- Specific concepts covered in the lesson
Examples: evaporation and condensation
English and metric units of volume, mass and length
Examples: truth and honesty
respect for other people
- Lesson objectives
- Materials needed
Reference books/websites
- Process/Procedures
- Introductory or Motivational activities
- The lesson proper
- Linkage with human values
- Closure
- Assessment/Evaluation
- Attachment :
- References
- Attachment 1 (Materials)
- Poem
- Song
- Folktale
- Other media
- Etc.
- Attachment 2 (Activity Sheet).
- Attachment 3 (Assessment sheet)
Attachments 1
Students Activity Worksheet
Name of teacher :
Grade/level :
School :
Subject Matter Area :

Topic :

Title of Activity :

Objective(s) of the activity:

Process and Steps
Process |
Steps |
Note: time, etc. |
Preparation for students to participate in the activities |
|
|
Activities:
Step by step guidance for students (incl. questions, and expected answers) |
|
|
Expected Results (what, in what forms, how and who to assess) |
|
|
Reflective Questions:
- What concepts, principles, procedures, skills have you learned?
- What do you want to learn more?
- General comments:
Students Activity Worksheet: Elaboration
Subject Matter Area : Please state, e.g., Biology, Physic, Chemistry, Science, Mathematics, etc.
Topic : Please state specific topic in any given subject matter area
Title of Activity : Please state specific title of the activity for students to carry on
Objective(s) of the activity:
Please state in behavioral terms
Process and Steps
Process |
Steps
(detail of steps) |
Note: time, etc. |
Preparation for students to participate in the activities: explanation of the preparatory activities needs to be done by the students, i.e. reading an article, boiling eggs, looking for an equipment, etc. |
|
(write down the approximate time needed for each steps, anticipated questions from students at each steps, questions posed by teachers, and anticipated answers to the questions). |
Activities:
Step by step guidance for students (incl. questions, and expected answers): explanation on step by step needs to be done by students in carrying out an activity, including forming a group, looking for books in the library, etc. |
|
Expected Results (what, in what forms, how and who to assess): explanation of the expected results of the activity (i.e., chart of observation, etc.) in various forms (multiple representation), and indicators of performance that are being used by teachers |
|
Reflective Questions:
These questions are to be answered by students after they participate in the activities as planned. It is a kind of reflection tool/guidance for the students about what they have learned, what they have not learned and want to know more, and their perception (evaluative comments) on the instructional activities they participated in.
- What concepts, principles, procedures, skills have you learned? (i.e.: concept map)
- What do you want to learn more?
- General comments.
Attachment 2
Assessment Sheet
Name of teacher : ___________________________________________
Grade/level : ___________________________________________
School : ___________________________________________
Subject Matter Area : ___________________________________________
Topic : ___________________________________________
Instructional Objective(s):

Assessment Procedures:
What |
How |
Who (Assessor) |
Knowledge |
|
|
Problem Solving Skills |
|
|
Scientific Inquiry Skills |
|
|
Affective/Attitude Expression |
|
|
Values Expression |
|
|
Personal Expression |
|
|
Scoring and Grading
How would you evaluate the student’s achievement? By score?, by grade?, by category (pass/fail, outstanding/good/fair/unaccepted)? Explain.
Assessment Sheet: Elaboration
Subject Matter Area : Please state, e.g., Biology, Physic, Chemistry, Science, or Mathematics
Topic :Please state specific topic in any given subject matter area
Instructional Objective(s):
Please state in behavioral terms
Assessment Procedures:
What |
How |
Who (assessor) |
Elaborate in detail knowledge to be learned by the students from a given topic through a given activities. |
Explain how the students will express their understanding in each category (through a poem, a poster, a writing, etc.), how explanation of their artifacts will be given by students (oral versus written), and how their understanding will be assessed (criteria being used) |
Who will be the assessor? Peer, teachers,
Students significant others? |
Problem Solving Skills
Elaborate problem solving skills to be learned by the students from a given topic through a given activities. |
Scientific Inquiry Skills
Elaborate scientific inquiry skills to be learned by the students from a given topic through a given activities. |
Attitude/Affective Expression
Elaborate affective or attitude expression expected to be demonstrated by the students |
|
|
Values Expression
Elaborate values expression expected to be demonstrated by the students |
|
|
Personal Expression
Elaborate personal expression (nurturant effect/incidental learning) expected to be demonstrated by the students. |
|
|
Evaluation:
How would you evaluate the student’s achievement? By score?, by grade?, by category (pass/fail, outstanding/good/fair/unaccepted)? Explain.
This section is to explain about the ways teacher goes about evaluating his/her students’ achievement. If it is by score, then interval of scores and their meaning must be explained in details. If it is by grade, each grade should have meaning and criteria for students to be able to follow. It is by category, then each category should has clear explanation of meaning and criteria for students to follow. |


