|
Project Monitoring and Evaluation Presented by Dr. Lilibeth F. Taa
Workshop Objectives At the end of the course, the participants should be able to: 1. Agree on the monitoring and evaluation framework for Project SEA WAVE.
2. Develop monitoring and evaluation tools to determine the effectiveness of the integrated HVWSHE teaching-learning materials.
3. Formulate guidelines for the assessment of integrated HVWSHE teaching-learning materials for use by teachers and principals.
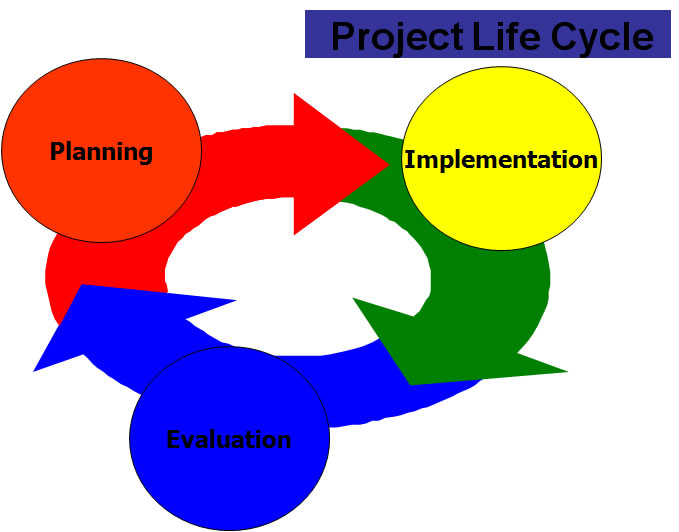
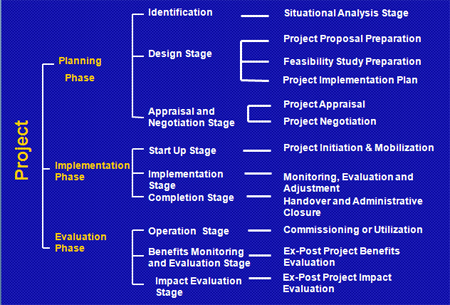
Project Cycle Management
Overview of Project Management
Definitions Monitoring refers to the continuous accumulation of information regarding progress towards an outcome. The objective is to track changes from baseline conditions to desired outcomes. Evaluation assesses what results were achieved, and how and why, they were or were not achieved. Why Conduct Project Monitoring and Evaluation? • To enhance organizational learning;
• To ensure informed decision-making;
• To support substantive accountability, i.e., to document for people in authority that desired goals are being met;
• To reposition an organization’s activities.
Outcomes-Based Monitoring & Evaluation Framework
Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation Discussion Outline: The language of Outcomes-Based M&E How to conduct effective Outcomes-Based M&E How to apply Outcomes-Based M&E on the effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials How to develop Outcomes-Based M&E tools to determine the effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials How to formulate guidelines for the assessment of Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials for use by teachers and principals.
The Language of Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation Defining Key Terms IMPACT - The “big picture” changes that the project is working toward.
- A preferred future
- Answers why the work is important
- Equivalent to goal and/or vision statements
Example: What impact is education having on students?
The Impact of Project SEA-WAVE To develop a new water-use ethic among South-East Asian citizens. The Language of Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation Defining Key Terms OUTCOMES - The concrete changes a program is trying to bring about
- A program is effective when it is able to bring about the expected outcome
- These concrete changes are intended to contribute to a project’s impact
- The results of interactions between individuals and schooling experiences
Example: What are the positive outcomes of schooling?
The Language of Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation Defining Key Terms INDICATORS - The evidence, or proof, needed to show progress toward outcomes.
- Indicators need to give accurate and reliable evidence
- The evidence has to be easy to gather and useful to those making management decisions.
- Can be quantitative or qualitative.
Example: How will you know that students demonstrate competence in communication?
How to Conduct Effective Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation 1. Clearly state the impact your project is working toward. 2. Specify outcomes and indicators. 3. Identify sources of data. Rely as much as possible on use of existing information.
Examples: school electric power consumption bills, state-wide or local survey results
Developing new data collection instruments and procedures requires a carefully considered process of: 1. design,
2. development,
3. field testing,
4. revision,
5. sampling,
6. training,
7. collection,
8. error checking,
9. data entry, and
10. analysis
How to Conduct Effective Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation 4. Design M&E methods and tools. Methods Documentary Analysis Testing Standardized Survey Observation Interview Focus Group Discussion Field Triangulation Use of metrics Tools
How to Conduct Effective Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation 5. Analyze data systematically. 6. Document achievements and challenges as they occur. 7. Generate lessons learned and adapt strategies accordingly. 8. Submit an M&E report to Program Management.
Applying Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation on the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials Outcomes-Based Monitoring and Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Use of Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials DRESSING UP THE OUTCOME-BASED MONITORING AND EVALUATION FRAMEWORK FOR PROJECT SEA-WAVE
Introduction: What is the background of the initiative to conduct monitoring and evaluation of Project SEA-WAVE?
Objectives: Why is it necessary to perform an M&E of SEA-WAVE?
The Monitor or Reviewer: Who will serve as monitors or reviewers?
Frequency and Scheduling of M&E: What will be a good schedule in conducting M&E? How frequent should M&E be done?
M&E arrangements Will all the teachers using the HVWSHE Teaching Learning Materials be included in the review?
What arrangements may be needed prior to the M&E? - notice - documents
How should actual M&E be conducted?
What should be done after conducting M&E? Outcomes-Based Monitoring & Evaluation Framework
Outcomes-Based Monitoring & Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials
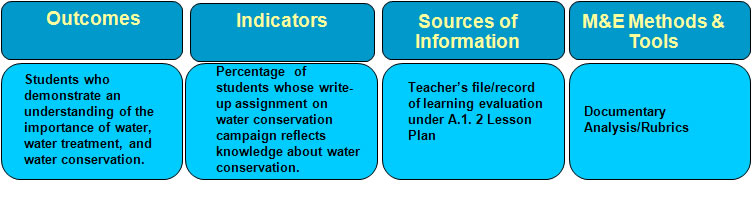
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
How to Develop Monitoring and Evaluation Tools on the Effectiveness of Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials How to Develop Monitoring and Evaluation Tools that will Help Determine the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials
Effectiveness Operationally Defined The effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Material is evidenced by its ability to produce the intended learning outcome among students.
Developing Outcomes-Based Monitoring & Evaluation Tools
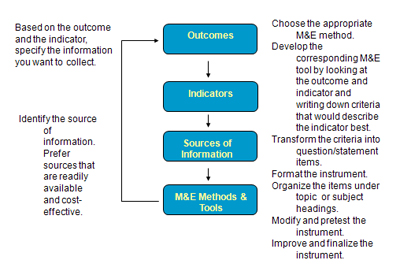
How to Develop Monitoring and Evaluation Tools that will Help Determine the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials Steps in Developing M&E Tools: 1. Based on the outcome and the indicator, specify the information you want to collect.
2. Identify the source of information. Prefer sources that are readily available and cost-effective
3. Choose the appropriate M&E method.
4. Develop the corresponding M&E tool by looking at the outcome and indicator and writing down criteria that would describe the indicator best. 5.Transform the criteria into question/statement items.
6.Format the instrument.
7.Organize the items under topic or subject headings.
8.Modify and pretest the instrument.
9.Improve and finalize the instrument.
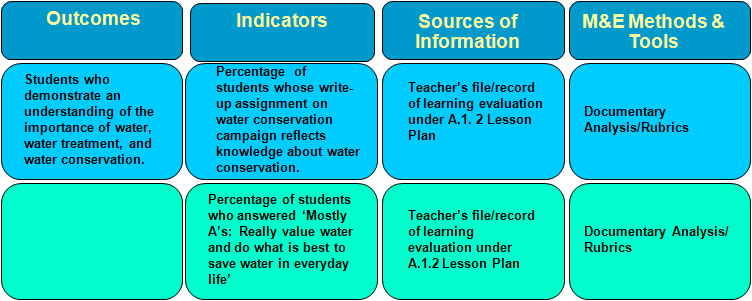
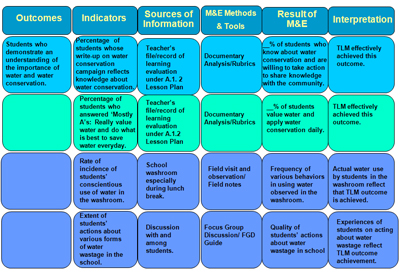
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
M&E Tool for Lesson Plan A.1.2
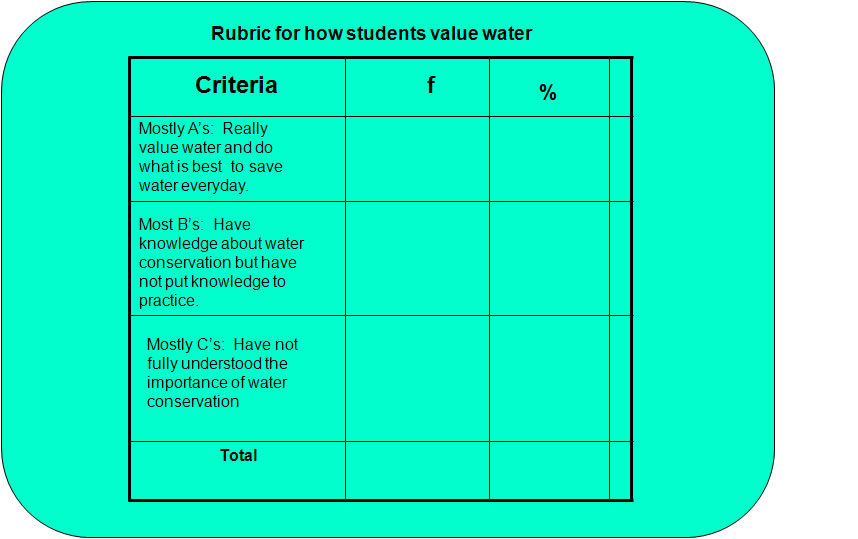
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
M&E Tool for Lesson Plan A.1.2
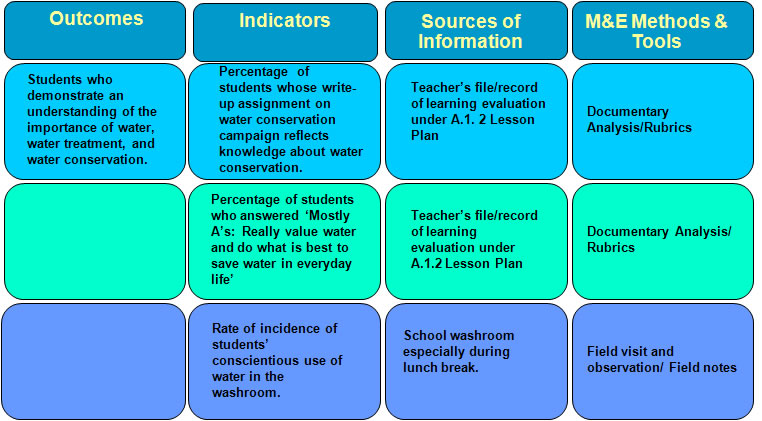
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
M&E Tool for Lesson Plan A.1.2
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
M&E Tool for Lesson Plan A.1.2 Focus Group Discussion on extent of students’ actions about various forms of water wastage in the school Date of FGD _____________ Time____ Venue _______________ Objectives of Discussion: 1.To find out if students have experienced taking action about forms of water wastage they have observed in the school.
2.To obtain students’ impressions and opinions about water wastage and their actions to address this .
Moderator’s Script: 1.First, in our discussion today, there is no right or wrong answer. We are interested in knowing your observations of how people in the school use water.
2.Second, you shouldn’t feel that you have to agree with everyone else in this room if that’s not how you really feel. There are 10 people in this room and we expect that people will have different views. And it’s important that we learn about all the views that are represented here.
3. Third, we want you to feel comfortable saying good things as well as critical things. We just want to understand your impressions of how people use water. 4. Fourth, we ask that you talk one at a time so that we can be sure to hear everyone’s views and get them on tape. Guide Questions: 1. What are the different uses of water in the school? 2.How do people in the school use water?
3.What water conservation practices do people in the school apply?
4.If they practice water conservation, what do you think are the reasons that they conserve water?
5.What can you say about their practice of water conservation?
6.What do people in the school practice that lead to wastage of water?
7.What do you think are the reasons that they waste water?
8.What can you say about the way that water is wasted?
9.Did you take action about the water wastage you observed? If yes, what did you do? If no, what is the reason that you did not take action?
10.If you would see forms of water wastage in the future, what will you do?
Formulating Guidelines for the Assessment of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials How to Formulate Guidelines for the Assessment of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials (TLM) In order to formulate guidelines for Principals and Teachers on how they will assess the effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE TLM, answering the following questions may be useful: 1.Before conducting an assessment of the effectiveness of the TLM, what preparatory activities would you suggest be done by the Principal (P)/Teacher (T)?
2.After the preparation, what should be done first by P/T in order to get a general idea of what the TLM is intended to do?
3.After getting the general idea, what should the P/T do?
4. What parts of the lesson plan should the P/T carefully take note of in order to know the outcome intended? 5. What part of the lesson plan tells about the possible indicator/s for the outcome intended?
6. Are there other indicators not provided in the lesson plan that the P/T could use?
7. When could the P/T say that the TLM is effective? 8.What qualitative output may be derived by the P/T through the monitoring and evaluation process?
9.What should the P/T with the M&E findings?
Guidelines for the Assessment of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials (TLM) 1. Before conducting an assessment of the effectiveness of the TLM, be ready with your HVWSHE TLM, your Outcome-Based Monitoring Framework, sheets of paper for note taking, and pencil. When the materials are ready, prepare yourself properly to begin the assessment. The right setting of ventilation and lighting and comfort, depending upon your working style is very important. 2. After the preparation, skim through the material in order to get a general idea of what the TLM is intended to do. Keep notes on sheets of paper of the organization of the TLM composed of several lesson plans. 3. After getting the general idea, reread the TLM specially focusing on the row headings Human values addressed and Lesson Objectives, particularly on the lesson objective reflecting the HVWSH learning outcome. 4. After taking note of the HVWSH learning outcome reflected, find the last row heading Assessment/Evaluation and check whether the evaluation is a good indicator of the achievement of the outcome. 5. If the given evaluation activity provides good indicator information, decide on the monitoring method that will best extract quantitative/qualitative data. Other indicators not mentioned in the lesson plan may also be included by the evaluator.
6. Based on the M&E method you will choose to apply, devise an appropriate tool. The tool you need may be a simple frequency table where number of students who obtained particular scores or responses, as the case may be, with the evaluation instrument. 7. Compare the data/information gathered with the Human values addressed and lesson objectives portions. If the data provide evidence that the outcome had been achieved, the TLM can be said to be effective. If the data do not show evidence of outcome achievement, the TLM had not been effective. 8.If the TLM had been effective, determine the factors contributory to its effectiveness and the lessons learned. If the TLM had not been able to achieve the outcomes, probe on the hindering factors and take note of lessons learned from the situation.
9. Prepare a monitoring report, keeping a copy for your file, and submit to Management.
OBME of the Effectiveness of the Integrated HVWSHE Teaching-Learning Materials: Water and Environmentally Sustainable Development Lesson Plan A.1.2
|